SECTION 1 : BIM BASIC CONCEPT
- Building Information Modeling – the coordinated workflow to input & produce a BIM Model.
- Building Information Model – evolving result of the coordinated inter-disciplinary input allowing a streamlined output
Build it twice – virtually and physically allowing for preemptive measures :
a) Clash detection between discipline (Arch, C&S and Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing Services etc)
- less variation order caused by coordination error
- more efficient
- end product more quality
b) Less coordination error and less correction on site.
c) The ability for technical and non-technical people to visualize the end product in a simulated environment.
SECTION 2 : BIM BASIC CONCEPT
High income nations -Private sector driven due to the high labour costs. BIM allows for a more efficient use of resources. Government enforcing began once the BIM workforce has matured.
- Industry
- government
The use of BIM allows for improvement of current construction process. These areas include affordability, sustainability, and stakeholder relationships/workflows. If elaborated according to stages (design, construction, operation and maintenance).
Design Stage
- Allows Client/Building Owner to evaluate the proposed design, and changes
- Better understanding of project at early stages
- Improved planning and design
- More upfront involvement of key stakeholders who can provide earlier feedback
- Intelligent transfer of information between key project stakeholders
- Greater certainty between design intent and the final construction and operation of the building
- Each project stakeholder has more informed design decisions at the beginning of the project.
- Improved efficiency for design production
- Improved ability for analysis and design audit
- Quicker client approvals via showing design intent
Construction Stage
- Better outcomes through collaboration
- Improves multi-party communication
- Reduced project risk
- Enhanced project performance
- Improved safety and quality
- Reduces unbudgeted construction changes
- Reduced waste
- Increased prefabrication
- Reduce unpredicted disruptions in the construction process.
- Increased transparency
- Real time coordination across disciplines
Operation and Maintenance Stage
- Procure and manage assets report at early stage
- Reduction in the lifecycle cost
- Elimination of defects
- Fewer and more predictable disruptions to business operations occur in a well-run facility.
- Digital facilities management, armed with a full complement of operation and maintenance information makes building operator reducing operating cost.
BIM Implementation stage (Figure 1) illustrates a blueprint for the BIM implementation stage in Malaysia. It represents the steps and progression of BIM implementation based on the progressive stages according to the level of maturity and capability of the industry.
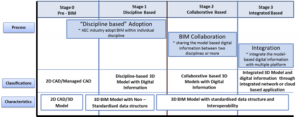
In general, the vertical columns of the BIM Implementation Stage in Malaysia indicate the main elements to guide the construction industry players in implementing BIM. The detail explanations of each stage are as in Table 1 below:-
| Stage 0 Pre-BIM (2D CAD/Managed CAD) |
|
| Stage 1 Discipline Based Model (Discipline-based 3D Model with Digital Information) |
|
| Level 2 Collaborative Based Model (Collaborative based 3D Modelc with Digital Information) |
|
| Level 3 Integrated Based Model (Integrated 3D Model and digital information through integrated network or cloud based application) |
|
SECTION 3 : IMPLEMENTATION OF BIM AT ORGANISATION LEVEL
- Assessing the BIM implementation requirement
- Policy, commitment and guidelines
- Establish BIM implementation team
- Determine infrastructure needs
Yes, however CIDB/JKR will assist in term of affordable software and hardware rental.
SECTION 4 : IMPLEMENTATION OF BIM AT PROJECT LEVEL
The objective of implementing BIM on a project level is to improve the quality, efficiency and safety through:-
- To improve the accuracy of design information. The accuracy of building design can be improved and design problems and conflicts between Architects, Civil Engineers and M&E can be resolved before the building was built. This can speed up the construction process.
- To build a 3D visual model for building and all the problems during construction can be detected much earlier and will save construction costs.
- To prepare the informational building model. With this preparation, any corrections or changes in design can be made earlier than that, any overlap between the disciplines of layout drawings can be detected.
- Facilities Management
The use of BIM can help system maintenance building (building life cycle). Any damage to building equipment can be replaced easily through the system information stored in the building BIM projects. This is to facilitates the maintenance of the building and hence to reduce maintenance costs.